Bibliographic Information]
Kei Akuzawa, Yusuke Iwasawa, Yutaka Matsuo. Estimating Disentangled Belief about Hidden State and Hidden Task for Meta-Reinforcement Learning. Learning for Dynamics and Control (L4DC) Conference. June 2021.
Overview
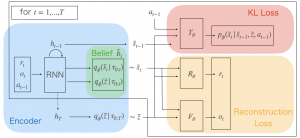
There is considerable interest in designing meta-reinforcement learning (meta-RL) algorithms, which enable autonomous agents to adapt new tasks from a small amount of experience. In meta-RL, the specification (such as reward function) of the current task is hidden from the agent. In addition, states are hidden within each task owing to sensor noise or limitations in realistic environments. To address this, we propose estimating disentangled belief about task and states, leveraging an inductive bias that To address this, we propose estimating disentangled belief about task and states, leveraging an inductive bias that the task and states can be regarded as global and local features of each task. Specifically, we train a hierarchical state-space model (HSSM) parameterized by deep neural networks as an environment model, whose global and local latent variables correspond to task and states, respectively. Because the HSSM does not allow analytical computation of posterior distribution, i.e., belief, we employ amortized inference to approximate it. After the belief is obtained, we can augment observations of a model-free policy with the belief to efficiently train the policy. Moreover, because task and state information are factorized and interpretable, the downstream policy training is facilitated compared with the prior Empirical validations on a GridWorld environment confirm that the HSSM can separate the hidden task and states information. Then, we compare the meta-RL agent with the HSSM to prior meta-RL methods in MuJoCo environments, and confirm that our agent requires less training data and reaches higher final performance.